Venture capitalists and other investors have poured capital into fintech startups around the world in recent years, including a record number of rounds worth $100 million or more in the second quarter of 2020. In Q2 2020 venture-backed fintech startups raised 28 nine-figure rounds, underscoring the scale of the bet investors are making on fintech’s long-term success.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. You can read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
Inside that fintech wave are various hubs of activity, including payments tech, investing and banking. That last category has helped give rise to so-called neobanks, startup banking entities that offer mobile-first, consumer-friendly banking tools and services. Given the old-fashioned nature of banking in many countries (and how far out of reach banking remains for many) neobanks have seen strong uptake by users in recent years.
And the startup cohort has raised oceans of capital to help fuel its growth. In America, Chime was most recently valued at $5.8 billion after raising hundreds of millions in late 2019. More recently, neobank Revolut added $80 million to its Q1 2020 round worth $500 million. Revolut is also worth north of $5 billion. Monzo is well-funded (albeit at a recent valuation reduction), Latin America-focused NuBank is worth $10 billion, according to Crunchbase, Starling recently raised another £40 million, while Germany’s N26 is worth over $3 billion after its most recent nine-figure round.
 From the fundraising perspective, then, neobanks are killing the game. And thanks to recent tailwinds from the COVID-19 pandemic that have bolstered interest in savings-related products, many of the same entities could be enjoying a strong year thus far. But recent self-reporting of some neobank’s 2019-era results details ample red ink — perhaps more than we might have anticipated.
From the fundraising perspective, then, neobanks are killing the game. And thanks to recent tailwinds from the COVID-19 pandemic that have bolstered interest in savings-related products, many of the same entities could be enjoying a strong year thus far. But recent self-reporting of some neobank’s 2019-era results details ample red ink — perhaps more than we might have anticipated.
Of course, startups don’t raise money for fun; they raise it to invest it in their operations and drive scale. So, we knew that these megafundraisers were losing money on purpose. All the same, let’s peek at the economics of several neobanks, as their now dated and thus not at all current results can provide useful context on two points: Why investors are excited to put their capital to work in neobanks, and why neobanks always seem to have another check to announce.
Monzo, Starling and Revolut
To prevent my receiving unhappy emails from irked fans of these companies, please bear in mind that we’re looking several quarters back when observing the following results.
It would be lovely to have more recent data, but with European neobanks reporting their — roughly — 2019 results in recent weeks, this is what we have. We are going to parse the numbers, but we will not conflate past performance with current results. We do not know much about 2020 neobank financial performance.
Anyhoo, to the numbers. You can read the full documents from Monzo here, Starling here (or here, if that link is struggling) and Revolut here.
Let’s start with Monzo, which has a clear set of figures for us to peek at:
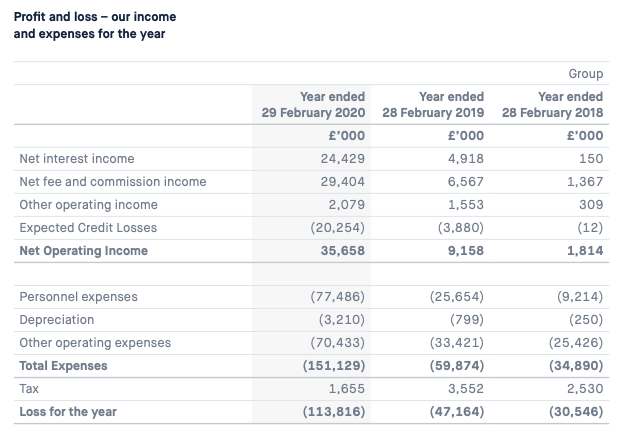
Image Credits: Monzo
Read the original post: Building a fintech giant is very expensive
Organize your team with Milanote.
